MH Energy Your Better Solar and Energy Partner
MH Energy Your Better Solar and Energy Partner
In an era where power outages can disrupt daily life, finding reliable solutions becomes essential. Battery backup for homes offers a safety net during unexpected electrical failures. These systems ensure that vital appliances and devices remain operational when the grid falters.
Choosing the right battery backup can be daunting. Many homeowners might overlook the varying capacities and technologies. Lithium-ion batteries are popular for their longevity, while lead-acid options remain cost-effective. It’s crucial to assess individual needs and power demands. A generator may provide temporary relief, but it doesn’t offer the convenience of seamless energy transition.
Imagining life without a functional refrigerator or internet can be unsettling. Families often experience frustration during outages. This can lead to spoilage of food and disruption of work-from-home arrangements. Investing in a quality battery backup for homes addresses these challenges head-on. However, one must regularly evaluate their chosen system. What works today may need an upgrade tomorrow. Balancing immediate needs with future growth is a lesson many homeowners learn.

When considering battery technologies for home backup, several options stand out.
Lithium-ion batteries are popular due to their high energy density.
They are compact and offer longer lifespan compared to other types. These batteries can efficiently store power from
renewable sources like solar panels. However, they can be costly, and their environmental impact raises questions.
Lead-acid batteries provide a more economical choice. They are widely used in
off-grid systems. These types are heavy and require regular maintenance.
Their shorter lifespan compared to lithium-ion is a drawback. While they can deliver substantial power, the need for
proper ventilation is often overlooked.
Saltwater batteries are an emerging technology. They are safer
and more environmentally friendly. However, their availability and performance consistency often come under scrutiny.
Many homeowners may find them less appealing due to limited data on
longevity and capacity. Each technology presents unique challenges. Understanding these nuances is critical for homeowners
facing power security decisions.
In the quest for reliable home power backup solutions, lithium-ion and lead-acid batteries are the main contenders. Lithium-ion batteries are lighter and have a higher energy density. They charge faster and last longer. However, they come with a higher upfront cost. Lead-acid batteries, while much cheaper, are bulkier and require more maintenance. They are less efficient and have a shorter lifespan compared to their lithium-ion counterparts.
When choosing between these two systems, it’s crucial to consider your specific needs. Think about how often you experience power outages. Assess the appliances you plan to support during an outage. Residential setups often require consistent and reliable power. Thus, efficient battery systems become essential.
Tips: Regularly check the battery health. Strive to maintain optimal temperature conditions. Consider investing in a system that allows for expansion in the future. It’s easy to overlook these factors, but doing so could save you headaches later on. The decision between lithium-ion and lead-acid isn’t merely about cost; it’s about what suits your lifestyle best. It might reflect your energy usage habits. Making the right choice requires deep consideration and reflection.
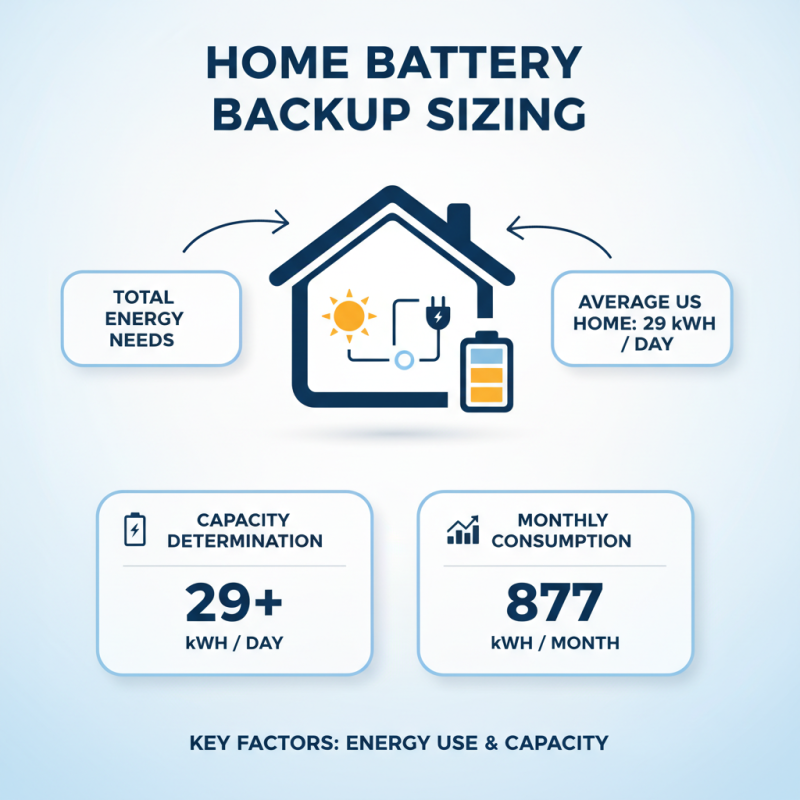
When sizing a home battery backup system, several key factors should be considered. The total energy needs of your household are essential. On average, American homes consume about 877 kWh per month, which translates to around 29 kWh per day. This figure helps determine the capacity your battery system should have.
Another crucial aspect is the duration of power outages in your area. In the U.S., homes experience about 3 hours of outages per year on average. However, this can vary significantly. If you live in a region prone to frequent storms, preparing for longer outages becomes necessary. Consider installing a system that can provide enough energy for critical devices over extended periods.
Power demands fluctuate throughout the day, often spiking during peak usage times. Understanding your peak demand will help size the inverter correctly. A well-sized system should handle these spikes without overloading. Balancing capacity and inverter ratings ensures efficiency and longevity. Reflections on your energy habits can lead to a more tailored and efficient battery backup solution.
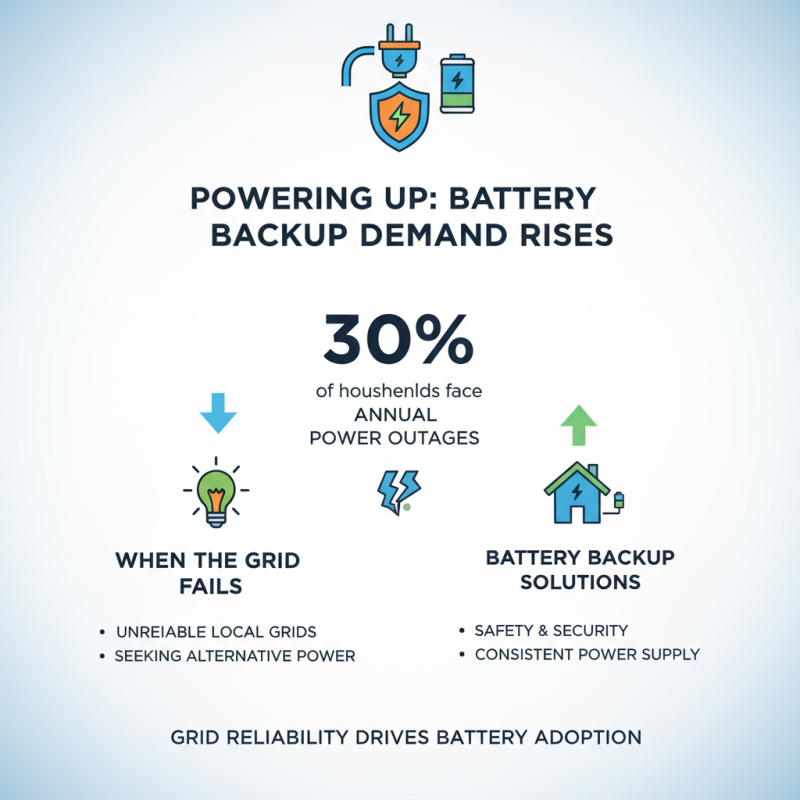
The reliability of local power grids significantly influences the demand for battery backup solutions. Recent studies show that nearly 30% of households experience power outages annually. This encourages homeowners to seek alternative power options. When the grid's reliability falters, people turn to battery backups for safety and security.
A notable report indicated that in regions with frequent outages, the adoption of battery storage systems increased by over 50%. In these areas, a reliable backup can prevent spoilage of food, continuity in work-from-home setups, and more. Homeowners often find themselves frustrated. They ask, "How can I ensure my home remains powered?" A battery backup could be the answer.
Tips: Assess your local grid's reliability. Investigate outage history for your area. Consider your energy needs. Smaller systems may not meet everyone's requirements. Flexibility in options is essential. Aim for a backup that adapts to your lifestyle and power needs. Balancing affordability with efficiency can be tricky, but it’s worth exploring.
Emerging innovations in home energy storage are changing how households approach power security. New technologies are designed to enhance efficiency and reliability. For instance, advanced lithium-ion batteries offer significant improvements over older models. These batteries have a higher energy density, enabling longer-lasting power solutions for homes.
Moreover, many systems are integrating artificial intelligence. Smart algorithms can predict energy consumption patterns, optimizing battery usage. This innovation can minimize waste and lower electricity costs. However, these systems still have a learning curve. Homeowners may need time to understand their full potential.
Another interesting development is solar integration. Homeowners can combine solar panels with energy storage systems. This setup allows for greater independence from the grid. Nonetheless, initial installation costs can be daunting. Many families hesitate before investing in these systems. Reflection on personal energy needs is essential for making informed choices.
| Battery Type | Capacity (kWh) | Cycle Life | Warranty (Years) | Charging Time (Hours) | Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium-ion | 10 | 2000 | 10 | 5 | 800 |
| Lead-acid | 7 | 500 | 5 | 8 | 300 |
| Nickel-cadmium | 6 | 1500 | 7 | 10 | 400 |
| Flow Battery | 12 | 10000 | 10 | 8 | 1500 |
| Lithium Iron Phosphate | 9 | 5000 | 10 | 4 | 700 |






