MH Energy Your Better Solar and Energy Partner
MH Energy Your Better Solar and Energy Partner
Solar energy has emerged as a pivotal force in today's renewable energy landscape. According to Dr. Emily Carter, a renowned expert in Solar Energy Solar, "Harnessing solar power is not just a trend; it’s a necessity for our planet's future." This highlights the urgency and significance of understanding how solar power works.
At its core, solar energy is derived from the sun's rays. Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity, providing a sustainable energy source. Many homes and businesses are embracing this technology. However, the transition is not without challenges. Issues such as installation costs and efficiency of panels must be considered.
Moreover, while solar energy presents a cleaner alternative, its production can also have environmental impacts. The materials used in solar panels require careful sourcing. Striking a balance between sustainable practices and effective energy production is essential. As we delve deeper into the workings of solar power, it’s vital to recognize both its potential and its limitations in shaping a sustainable future.

Solar energy is a vital renewable resource derived from the sun's rays. This form of energy plays a crucial role in combating climate change. As concerns about fossil fuels grow, solar power emerges as an effective alternative. Using sunlight to generate electricity can reduce dependence on non-renewable resources.
Solar energy systems convert sunlight into usable energy. Photovoltaic cells absorb sunlight and transform it into electricity. This process doesn’t emit carbon dioxide or pollutants, making it environmentally friendly. Many homes and businesses are moving towards this clean energy source. It’s a shift toward sustainability that many find inspiring.
However, solar energy is not without its challenges. The initial cost of installation can be high. Also, solar power generation depends on the availability of sunlight. In regions with less sun, this energy source may not be as effective. Regular maintenance is also required to ensure efficiency. Solar power technology continues to develop, yet it requires ongoing reflection and improvement.
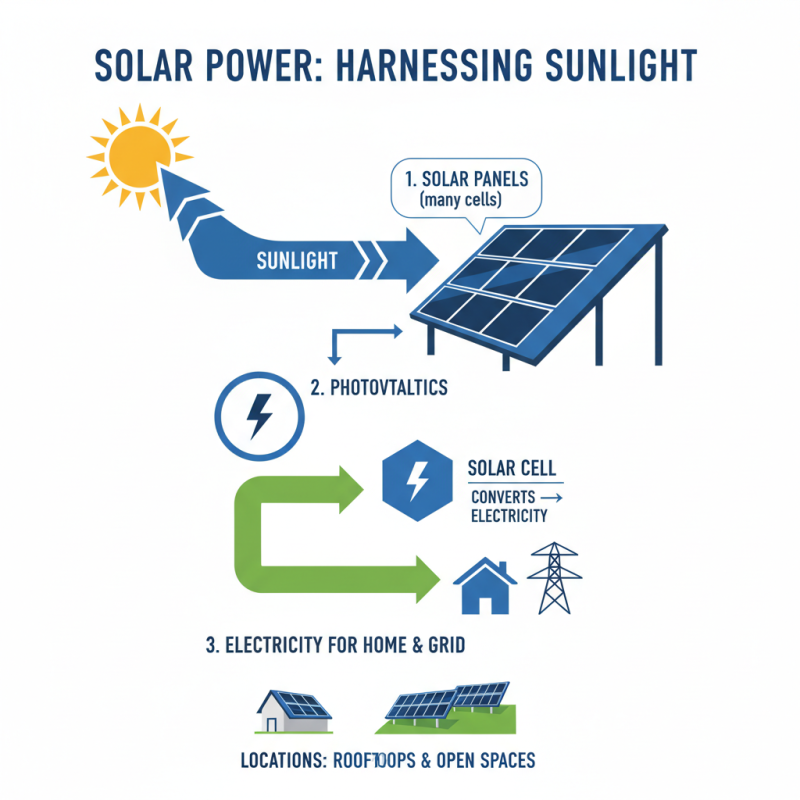
Solar power systems capture sunlight through a process called photovoltaics. These systems consist of solar panels, which contain many solar cells. Each cell converts sunlight into electricity. The solar panels are installed on rooftops or open spaces to maximize exposure to sunlight.
It's essential to consider the angle and placement of your solar panels. They should face the sun directly for optimal energy capture. Adjusting the tilt of the panels will also make a difference in efficiency.
Tip: Regular maintenance is key to efficiency. Clean panels ensure maximum sunlight absorption. Additionally, check for any shading from nearby trees or buildings.
Solar systems can sometimes underperform due to factors like weather or dirt. Understanding these variables helps with better energy management. Don’t rush into a decision; evaluate your space and energy needs carefully.
Solar energy is a renewable resource derived from the sun. The process of converting sunlight to electricity involves several key steps. Initially, solar panels capture sunlight using photovoltaic cells. These cells consist of semiconductor materials that absorb photons from sunlight. When sunlight hits these cells, it excites electrons, generating direct current (DC) electricity.
The next step involves inverters, which convert the DC electricity into alternating current (AC) electricity. This type of electricity is what powers most homes and appliances. While this technology is efficient, it does have its flaws. Not every sunny day guarantees optimal performance due to factors like shading or dirt on the panels. Also, energy storage can be challenging. Battery systems can be expensive and may not always work efficiently.
Finally, the electricity generated can be used immediately or fed back into the grid. This creates a two-way system, allowing for potential energy credits. However, not all regions have favorable policies. Thus, regulations can vary, impacting broad adoption. Embracing solar energy requires considering both its benefits and limitations.
| Dimension | Description | Value/Information |
|---|---|---|
| Solar Energy Definition | Renewable energy derived from the sun's radiation | Power source for electricity, heating, and more |
| Types of Solar Power Systems | Different configurations for energy production | Photovoltaic (PV) & Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) |
| Photovoltaic Cell Function | Conversion of sunlight directly to electricity | Utilizes semiconductor materials |
| CSP Technology | Uses mirrors to concentrate sunlight | Generates heat to produce steam for electricity |
| Benefits of Solar Energy | Advantages of using solar power | Sustainable, reduces electricity bills, low carbon footprint |
| Limitations of Solar Energy | Challenges in solar energy usage | Intermittent energy supply, high initial costs |
Solar energy is harnessed through two main technologies:
photovoltaic (PV) systems and
thermal systems.
Photovoltaic systems convert sunlight directly into electricity using solar cells. These cells are made of semiconductor materials that allow them to absorb sunlight and create an electric current. It's a straightforward process, but the efficiency of PV systems can vary. Weather conditions, shade from trees, and the angle of installation affect performance.
On the other hand, thermal systems utilize sunlight to generate heat. These systems often feature solar panels that heat a fluid, which can be used for heating water or driving steam turbines. The technology is effective for heating applications but can require a
large area for installation. In some cases, storage solutions are needed to manage energy supply during cloudy days or nighttime.
Both PV and thermal technologies have distinct
advantages. Yet, each faces challenges like efficiency limitations and space requirements. It's essential to evaluate where improvements can be made. Understanding the specific applications and limitations can guide better energy decisions in the future.
Solar energy's potential remains vast, but it's a field that requires continual learning and adaptation.
Solar power offers numerous benefits and challenges that are worth considering. One key benefit is its capacity to reduce energy bills. According to a report by the U.S. Department of Energy, solar energy systems can lower electricity costs by as much as 30%. This can significantly alleviate financial pressure on households and businesses alike. Another advantage is the positive environmental impact. Solar energy generates electricity with very low carbon emissions. This is crucial for combatting climate change.
However, challenges exist. Initial costs for solar panels can be high. Many people may feel discouraged to invest. A recent study found that the average upfront cost of a residential solar system is around $15,000. Additionally, solar power generation is dependent on sunlight, making it less reliable in certain weather conditions. This intermittency can complicate energy management and requires backup systems.
Tips: Consider using solar power calculators online to estimate savings. Engage with local solar energy organizations for insights. They can provide clarity on potential incentives. Balancing these factors is essential for a well-informed decision on solar energy adoption.






