MH Energy Your Better Solar and Energy Partner
MH Energy Your Better Solar and Energy Partner
As our understanding of the Solar Solar System deepens, we uncover layers of complexity and wonder that continue to captivate scientists and enthusiasts alike. The Solar Solar System, a colossal expanse housing planets, moons, asteroids, and comets, offers insights into the formation and evolution of celestial bodies. According to a recent report by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), the exploration of this vast system has led to significant discoveries, such as the determination of how the planets interact and the influence of solar winds on their atmospheres.
Dr. Emily Cartwright, a renowned astrophysicist at the Space Research Institute, emphasizes the importance of ongoing research into our Solar Solar System, stating, "Every mission to explore the Solar Solar System provides us with invaluable knowledge that propels our understanding of not only our planetary neighbors but also the fundamental processes that govern the cosmos." In light of these explorations, it's essential to highlight some of the most fascinating facts that often remain unknown to the public. From the quirky characteristics of our neighboring planets to the enigmatic phenomena occurring in the Kuiper Belt, the wonders of the Solar Solar System are both intriguing and vital to the future of space exploration.
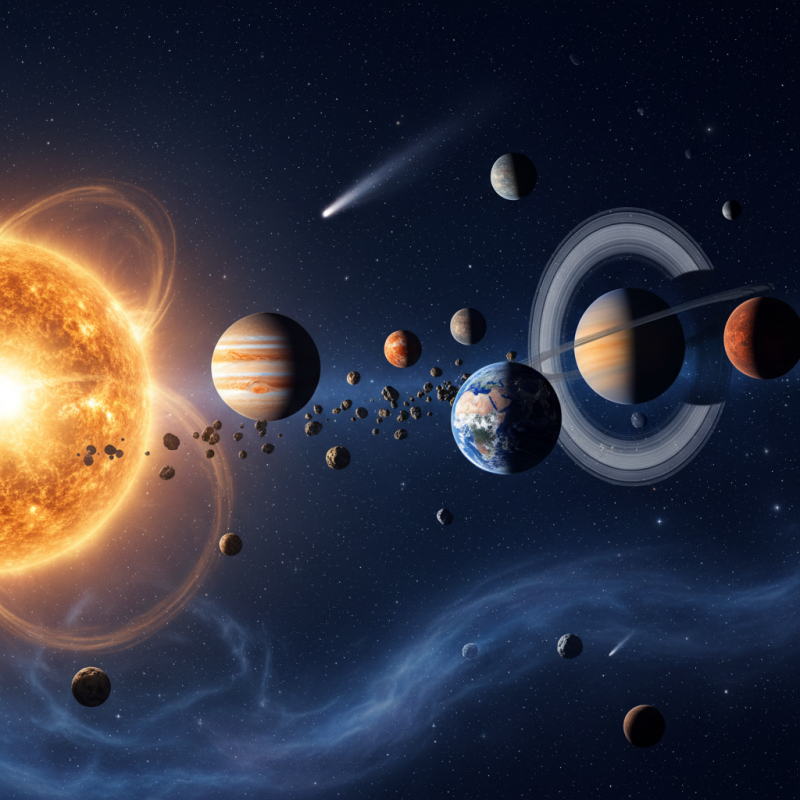

The solar system is a fascinating tapestry of diverse planets, each with its unique composition and characteristics. Starting with the inner planets, Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars, we find rocky surfaces rich in minerals and metals. Mercury, the smallest planet, has an iron core, making it highly dense, while Venus, shrouded in thick clouds of sulfuric acid, is known for its extreme greenhouse effect, resulting in scorching temperatures. Earth, our home, stands out with its abundant water and life-supporting atmosphere, while Mars captivates with its iron oxide-rich soil, giving it a distinct reddish hue.
In contrast, the outer planets – Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune – are predominantly gas giants, exhibiting vastly different compositions. Jupiter, the largest planet, is mostly made of hydrogen and helium, with a possible rocky core, while Saturn, famed for its stunning ring system, shares a similar gaseous composition. Uranus and Neptune, classified as ice giants, contain a greater proportion of elements like water, ammonia, and methane, giving them a unique bluish appearance. This varying composition among planets not only reflects the conditions under which they formed but also influences their atmospheres, surface conditions, and potential for hosting life. The unique characteristics of each planet contribute to the dynamic nature of our solar system, offering endless opportunities for exploration and discovery.
The solar system is home to a plethora of moons, many of which remain relatively unknown compared to their more famous counterparts. For instance, consider the intriguing moons of the gas giants like Uranus and Neptune. Uranus boasts 27 confirmed moons, with some of the most fascinating being Miranda and Umbriel. Miranda, with its dramatic cliffs and varied geological features, demonstrates a history of intense tectonic activity, suggesting a complex past that is still being unraveled by scientists. Recent studies have indicated that Miranda's surface is a mix of both ancient and young terrains, hinting at past resurfacing events possibly triggered by gravitational interactions.
On the other hand, Neptune's largest moon, Triton, is unique due to its retrograde orbit, a characteristic that sets it apart from nearly all other moons in the solar system. This unusual motion implies that Triton may have been captured by Neptune's gravity rather than having formed in orbit around it. Data from NASA's Voyager 2 mission reveals that Triton is geologically active, featuring geysers that expel nitrogen gas, indicating that it could harbor a subsurface ocean. According to recent planetary science reports, Triton’s distinctive traits and potential for hosting extraterrestrial life make it a subject of intense research and interest within the scientific community.
The Kuiper Belt is a vast region of our solar system that extends from the orbit of Neptune, about 30 astronomical units (AU) from the Sun, to approximately 55 AU. This area is populated by a plethora of icy bodies, including dwarf planets like Pluto and Haumea, as well as a myriad of small celestial objects. The Kuiper Belt plays a critical role in the dynamics of the solar system, acting as a boundary between the inner solar system, composed primarily of terrestrial planets, and the outer regions, which are dominated by gas giants.
One of the fascinating aspects of the Kuiper Belt is its influence on planetary formation and migration. It is believed that the materials within this region provided essential building blocks for the formation of the outer planets. Additionally, gravitational interactions between objects in the Kuiper Belt and the larger gas giants can lead to significant changes in orbits over time, potentially sending some objects into the inner solar system and creating a dynamic environment that continues to evolve. This intricate ballet of gravitational forces highlights the Kuiper Belt's importance in not only understanding the history and evolution of our solar system but also in predicting the future movements of celestial bodies within it.
Asteroids and comets are among the most intriguing remnants of our solar system's formation, offering a glimpse into the solar system's ancient history. These small celestial bodies, primarily found in the asteroid belt and the Kuiper Belt, are like time capsules, preserving material from the early solar system that dates back over 4.5 billion years. While planets formed through gradual accumulation of gas and dust, asteroids and comets remained relatively unchanged, providing scientists with invaluable insights into the conditions and processes that shaped our cosmic neighborhood.
Comets, composed primarily of ice and dust, ignite the imagination with their vivid tails and spectacular appearances. When they approach the Sun, the heat causes their ices to vaporize, releasing gas and dust that forms a glowing halo. This transformation not only gives comets their unique look but also suggests that they could be a source of water and organic compounds, which may have played a crucial role in the emergence of life on Earth. Similarly, asteroids, often metallic or rocky, can tell scientists about the primordial materials that make up planetary cores and surfaces. By studying these ancient relics, researchers are piecing together the puzzle of our solar system's history and understanding the processes that govern planetary formation.
The Sun plays a crucial role in our solar system, influencing not just the weather on Earth but also the behavior of other celestial bodies. Beyond providing light and heat, the Sun's gravitational pull keeps the planets in orbit and its solar wind affects the space environment. This interaction leads to a dynamic system where the Sun constantly emits charged particles that can interact with planetary atmospheres, creating stunning auroras and even impacting satellite communications.
To fully appreciate the Sun’s influence, consider how it shapes our climate and weather patterns. The solar cycle, which lasts about 11 years, influences solar activity, including sunspots and solar flares. These phenomena can increase solar radiation and have cascading effects on the Earth's atmosphere, potentially altering climate and weather systems.
Tips for observing solar phenomena: Always use proper solar filters or eclipse glasses when viewing solar events to protect your eyesight. Additionally, consider using a solar telescope or participating in local astronomy clubs to gain insights and firsthand experiences when observing sunspots or solar flares. Engaging with fellow enthusiasts can enhance your understanding of these captivating cosmic events and their effects on our planet.






