MH Energy Your Better Solar and Energy Partner
MH Energy Your Better Solar and Energy Partner
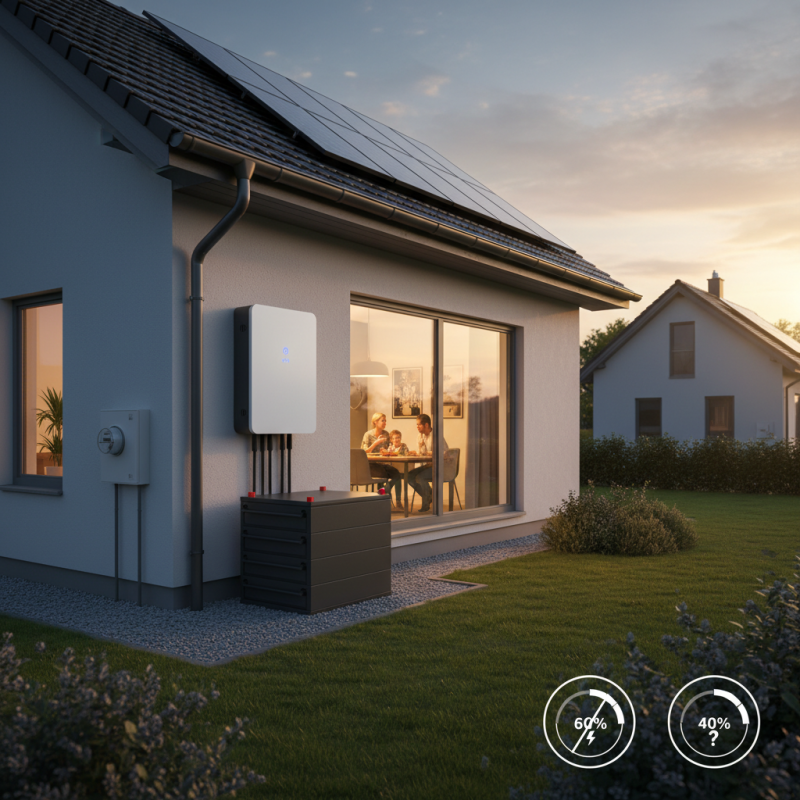
In today’s world, the importance of having a reliable Battery Back Up For Homes cannot be overstated. According to a recent survey by the Edison Electric Institute, about 60% of homeowners experienced at least one power outage last year. These interruptions can disrupt daily life, leading to inconvenience and potential financial loss. As such, investing in a robust battery backup solution becomes crucial.
Choosing the right battery backup involves consideration of various factors. Capacity, efficiency, and battery life are vital elements to analyze. Reports show that nearly 40% of homeowners are unaware of how to assess these features, often leading to oversight in their energy backup planning. Moreover, the average battery backup system's lifespan averages about 5 to 15 years, which requires careful thought on replacement schedules.
It's essential to reflect on personal energy needs and specific use cases. Some homes might need more capacity due to larger appliances. Others may find smaller systems sufficient. Ultimately, understanding the nuances of Battery Back Up For Homes can equip homeowners with a sense of security against unpredictable power outages.

When choosing a battery backup for your home, understanding your power needs is crucial. A study by the U.S. Energy Information Administration shows that the average American home uses about 877 kWh per month. This data provides a benchmark for evaluating how much backup power you’ll require during an outage.
Assessing your specific needs entails calculating your essential appliances' total wattage. For instance, a refrigerator needs around 100-800 watts, while a Wi-Fi router requires only about 10-20 watts. Keep in mind that cumulative power requirements can add up quickly. Thus, determining which devices you cannot do without is necessary.
Tips: Consider investing in a power meter to measure the wattage of your devices. This can help fine-tune your calculations and provide an accurate picture.
Assessing your needs isn’t just about numbers. It involves understanding your lifestyle. Do you rely heavily on medical devices? Then a robust system may be non-negotiable. Yet, can you compromise on powering some less critical items? This can inform your decision on battery capacity.
Tips: Always have a backup plan for your backup. Regularly test your battery system to ensure it operates smoothly. Ignoring maintenance can lead to unpleasant surprises when power outages happen.
Battery backup systems are essential for homes that experience power outages. There are several types available, each with unique features to consider. The most common types include lead-acid batteries, lithium-ion batteries, and salt-water batteries. Lead-acid batteries are affordable but have a shorter lifespan. They typically last around 5-7 years, while lithium-ion batteries can last up to 15 years or more. According to a recent industry report, the demand for lithium-ion batteries is projected to grow by 20% annually.
Salt-water batteries offer an eco-friendly alternative. They use saltwater as an electrolyte, making them less toxic compared to other types. However, they have lower energy density and take longer to charge. As you choose, consider your power needs and usage patterns.
Tip: Assess your energy consumption before selecting a battery system. Calculate watt hours required to support essential devices during an outage.
Incorporating battery storage with solar panels can be an excellent choice. This combination can save on energy bills and provide power during outages. However, installation costs can be high. Make sure to evaluate the total cost vs. long-term savings. It's crucial to weigh your options carefully. Not all systems fit every home.
| Battery Type | Capacity (Ah) | Voltage (V) | Expected Lifespan (Years) | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lead-Acid | 100 | 12 | 3-5 | Cost-effective, widely available | Heavy, shorter lifespan |
| Lithium-Ion | 200 | 48 | 10-15 | Long lifespan, lightweight | Higher cost |
| Nickel-Cadmium | 150 | 12 | 5-7 | Good performance in extreme conditions | Toxic materials, higher maintenance |
| SLA (Sealed Lead Acid) | 150 | 12 | 3-5 | Maintenance-free, easy installation | Limited cycle life |
| Flow Batteries | 300 | 48 | 10-20 | Scalable, long-lasting | Complex system, larger footprint |
Choosing the right battery backup for your home involves understanding several key factors. Capacity is crucial. This refers to how much energy a battery can store. A larger capacity means longer usage time during outages. Think about your needs. Do you want to power essential appliances only, or everything?
Another important factor is battery type. Lithium-ion batteries are popular due to their efficiency. They last longer and require less maintenance. Lead-acid batteries are cheaper but can be bulky and wear out faster. Assess your space. Some batteries are compact, while others require more room.
Consider the installation and integration. Can you set it up yourself, or will you need help? Some systems connect to solar panels, which is a plus if you plan for renewable energy. Realize that not every battery suits every home. Aim to match your home’s energy needs with what the market offers. Sometimes, the cheapest option can lead to disappointment later. Reflect on your lifestyle and power requirements before making a choice.
When choosing the best battery backup for homes, evaluating battery capacity and runtime is crucial. Battery capacity is typically measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). This measure indicates how long a battery can supply power. For example, a 10 kWh battery can power a 1 kW load for 10 hours. However, energy consumption varies from home to home. Many households use approximately 30 kWh daily, making it essential to select a system that meets individual needs.
Runtime is another critical factor. The average home power outage lasts about 2-3 hours, but some can extend for days. It's vital to assess how long you want the battery to provide power. Many users underestimate their needs. A report by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory notes that about 30% of battery systems are underutilized. This underutilization can result in inadequate power during extended outages. Understanding personal energy use can ensure you choose the right capacity and runtime.
It's also important to consider peak usage times. For instance, many homes consume more energy during evening hours. A battery backup must be able to handle these peaks effectively. Some experts recommend a buffer of at least 20% capacity above your estimated needs. This buffer can help accommodate unexpected surges in demand. In the end, selecting the right battery backup is about balancing capacity, runtime, and real-world energy consumption.
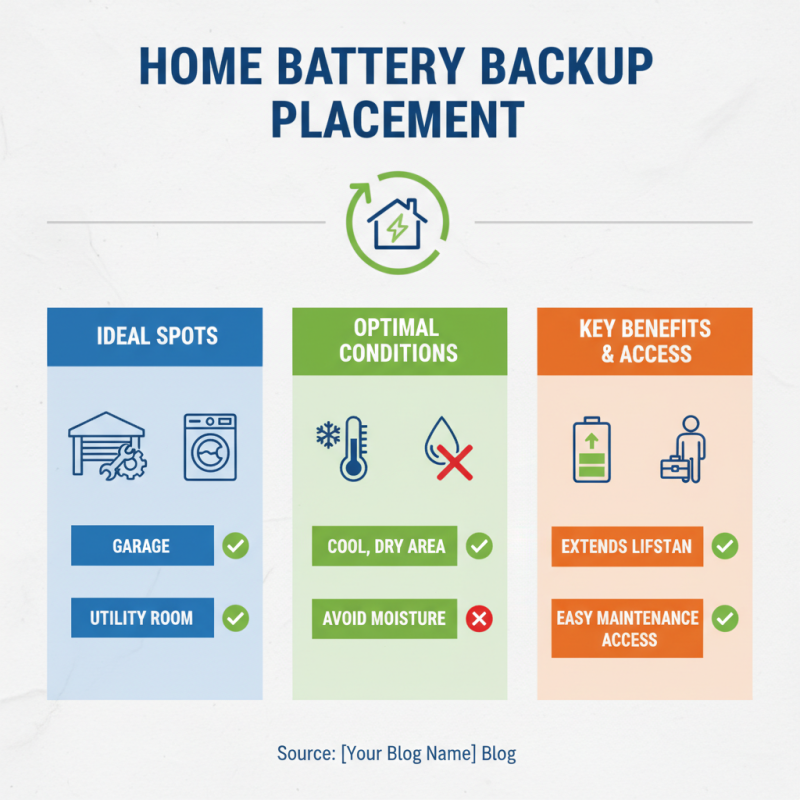
When installing a battery backup system at home, proper placement is crucial. Ideally, place the battery in a dry, cool area. This helps extend its lifespan. Avoid areas with high moisture. A garage or utility room can be good options. Ensure it's easily accessible for maintenance.
Regular maintenance is key. Check battery connections every few months. Look for corrosion or loose wires. Clean them gently with a cloth if needed. Ensure the batteries are not overly charged or deeply discharged. Over time, this can damage the system.
Tips: Monitor any unusual sounds or smells from the battery. They can indicate an issue. Schedule a professional inspection annually. This can prevent serious problems down the line. A proactive approach can save money in repairs. Regular checks ensure that your system is ready when you need it most.






